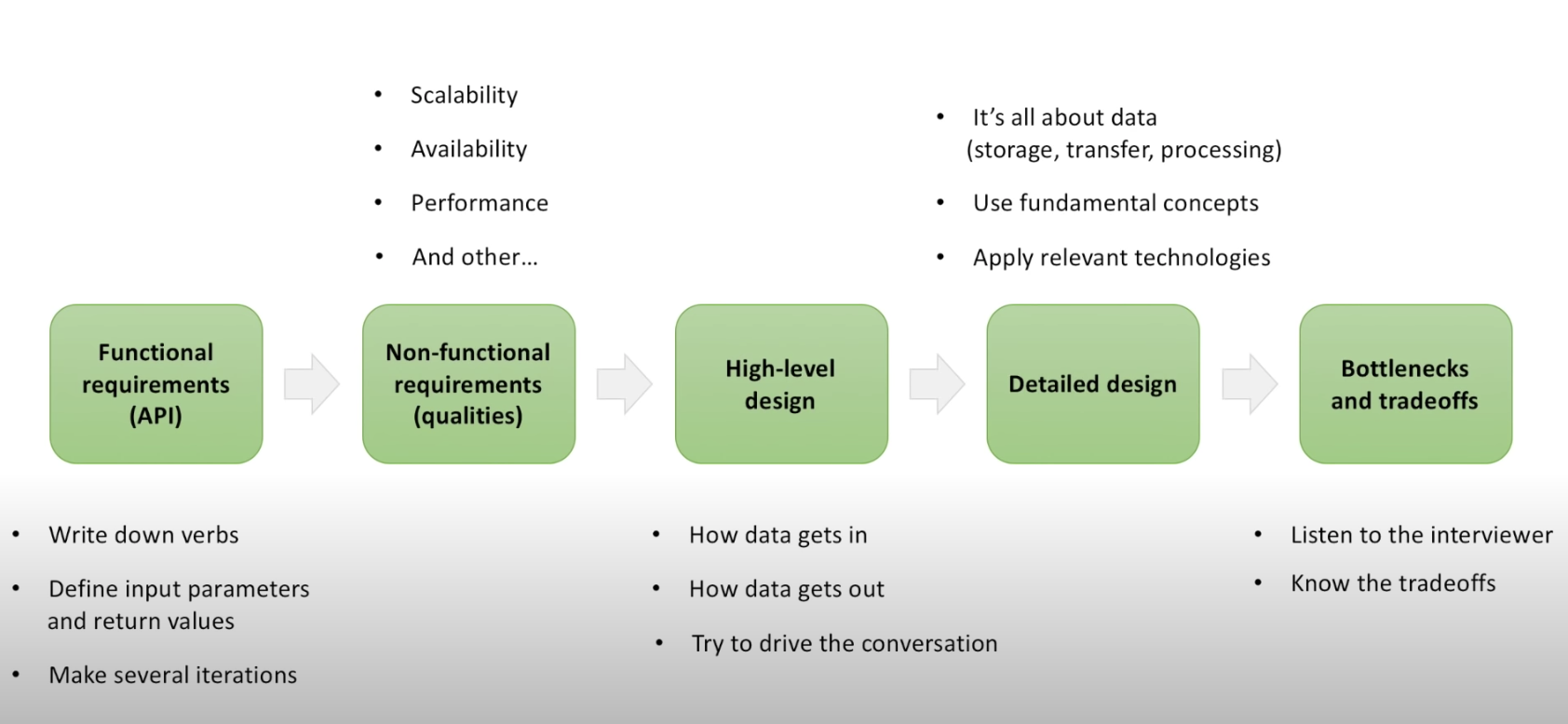
System design
System design involves 6 steps:
- Functional requirements (API)
- Non-functional requirments (quality)
- High level design
- Detailed design
- Bottlenecks and tradeoffs
Requirement clarification
In requirement clarification, focus on 4 key areas:
- User/customers
- Scale (read/write)
- Performance
- Cost
| User | Scale | Performance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Who/how | QPS/TPS, size/query, spike | p99 latency, write to read delay | development/maintenance |
Function vs non-function
Functional requirements
Non-function requirements
- Scalability
- High availability
- High performance
High level design
High level design covers the big picture workflow and services
- Data and store
- Processing
- High level architecture diagram
Store design
- What to store?
- Data
- Data schema
- Requirements: read/write, latency, scalability, availability, fail-over
- Transaction or analysis?
- Where to store?
- Compare db options related to non-function requirements
- How to scale write/read
- How to make both read/write faster?
- How not to lose data
- How to maintain data consistency?
- How to make sure data integrity?
- How to store?
Processing
- How to scale? Partitioning
- How to achieve high throughput? In-memory(cache)
- How not to lose data? Replication
- What to do when database is unavailable or slow? Replication/checkpoint
Problem 1: Aggregate data
- Should we pre-aggregate data in processing logic?
- Design 1: 3 updates, 3 count increase to database (3 x +1)
- Design 2: 3 updates, processing logic aggregate them, 1 increase to database (+3)
- Choice: design 2
- Push or pull
- push model won’t handle situation when processing unit fails
- push model won’t scale when processing unit takes long time to process
- pull model adds queue/persistency between event source and processing units, avoid both problems.
- checkpointing: queue remembers the offset for each consumer to ensure sequence and failover
- partitioning:
Detailed design for processing
- Deduplication cache
Ingestion path
- API
- blocking vs non-blocking I/O
- Buffering and batching
- Timeouts
- Retries with exponential backoff and jitter
- circuit breaker
- Load balancer
- Software vs hardware LB
- Network protocol
- LB algorithm
- DNS: avoid LB single point of failure
- Health checking (HTTP 200 response?)
- High availability (primary LB, replica LB)
- Partition service and partition
- partition strategy
- service discovery
- server side discovery: partition registers itself to ZooKeeper
- client side discovery: load balancer - Replication - Message format: backward compatibility
- json
- protobuffer
- thrift
Retrieval path
Tech stack
Client-side
- Netty
- Netflix hystrix
- Polly
Load balancer
- NetScaler
- NGINX
- AWS ELB
Messaging systems
- Apache kafka
- AWS kinesis
- AWS SQS
Data processing
- Apache Spark
- Apache Flink
- AWS kinesis Data Analytics
Storage
- Cassandra
- HBase
- Hadoop
- AWS redshift
- AWS dynamodb
- AWS S3
Cache
- Redis/Memcached
Master
- ZooKeeper
Monitoring
- AWS cloudwatch
- ELK
Paritition
- Consistent hashing
- Murmur hashing
Bottlenecks and tradeoffs
How to identify bottlenecks? How to monitor system health? How to make sure results accurate?