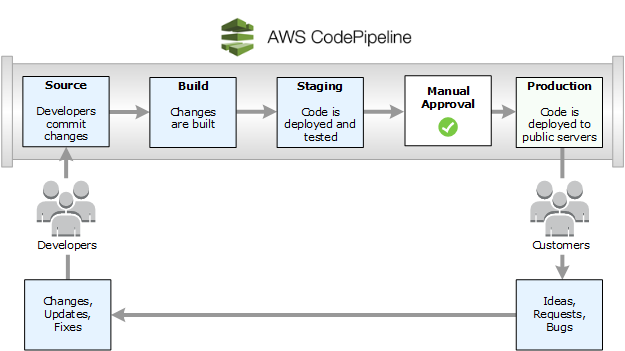
AWS code pipeline
Basic concepts
Modeling and configuring automated release process requires concepts and terms used in AWS CodePipeline.
- Pipeline
A pipeline is a workflow construct that describes how software changes go through a release process. Each pipeline is made up of a series of stages.
- Stage
A stage is a logical unit used to isolate an environment and to limit the number of concurrent changes in that environment. Each stage contains actions that are performed on the application artifacts.
- Actions
An action is a set of operations performed on application code and configured so that the actions run in the pipeline at a specified point. Valid CodePipeline action types are source, build, test, deploy, approval, and invoke.
- Pipeline executions
An execution is a set of changes released by a pipeline. Each pipeline execution is unique and has its own ID.
While a pipeline can process multiple executions at the same time, a pipeline stage processes only one execution at a time. To do this, a stage is locked while it processes an execution. Two pipeline executions can’t occupy the same stage at the same time.
Pipeline executions traverse pipeline stages in order. Valid statuses for pipelines are InProgress, Stopping, Stopped, Succeeded, Superseded, and Failed.
- Transitions
A transition is the point where a pipeline execution moves to the next stage in the pipeline.
- Artifacts
Artifacts refers to the collection of data, such as application source code, built applications, dependencies, definitions files, templates, and so on, that is worked on by pipeline actions. Artifacts are produced by some actions and consumed by others.