AOP in Java
Basic concepts
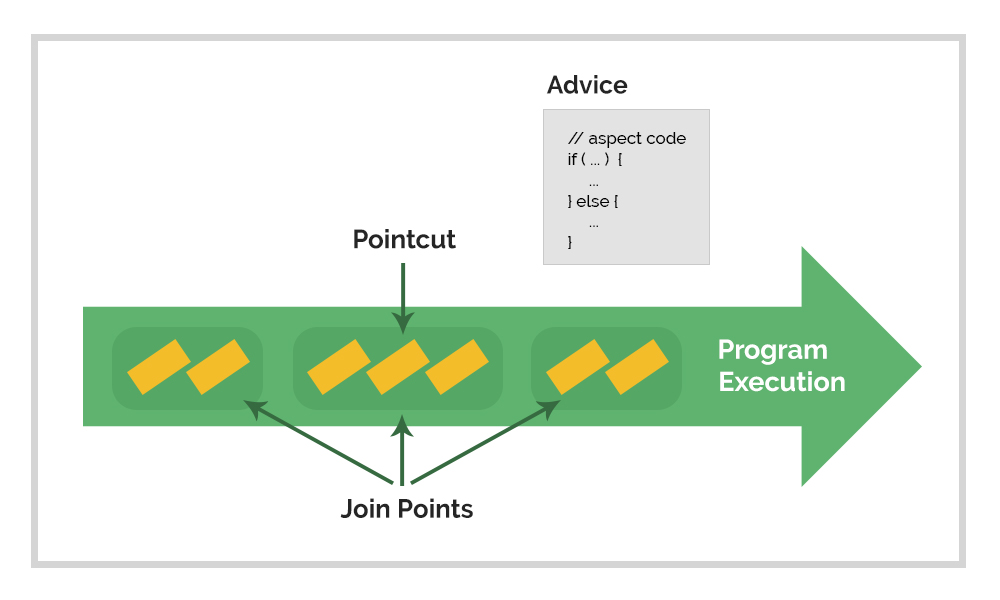
Aspect
Aspect is a modularization of a concern that cuts across multiple objects. For example, transaction management, logging, security, etc.
In Spring AOP, aspects are implemented using regular classes (the schema-based approach) or regular classes annotated with the @Aspect annotation (@AspectJ style).
Join point
A joint point is a point during the execution of a program, for example, the execution of a method or the handling of an exception.
In Spring AOP, a join point always represents a method execution. Join point information is available in advice bodies by declaring a parameter of type org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint.
Advice
Advice is an action taken by an aspect at a particular join point.
Different types of advice include “around,” “before” and “after” advice. Advice types are discussed below. Many AOP frameworks, including Spring, model an advice as an interceptor, maintaining a chain of interceptors “around” the join point.
- Before advice: Advice that executes before a join point, but which does not have the ability to prevent execution flow proceeding to the join point (unless it throws an exception).
- After returning advice: Advice to be executed after a join point completes normally: for example, if a method returns without throwing an exception.
- After throwing advice: Advice to be executed if a method exits by throwing an exception.
- After (finally) advice: Advice to be executed regardless of the means by which a join point exits (normal or exceptional return).
- Around advice: Advice that surrounds a join point such as a method invocation. This is the most powerful kind of advice. Around advice can perform custom behavior before and after the method invocation. It is also responsible for choosing whether to proceed to the join point or to shortcut the advised method execution by returning its own return value or throwing an exception.
Pointcut
A pointcut is a predicate that matches join points.
Advice is associated with a pointcut expression and runs at any join point matched by the pointcut (for example, the execution of a method with a certain name). The concept of join points as matched by pointcut expressions is central to AOP: Spring uses the AspectJ pointcut language by default.
Introduction
Introduciton, also known as an inter-type declaration, declares additional methods or fields on behalf of a type.
Spring AOP allows you to introduce new interfaces (and a corresponding implementation) to any proxied object. For example, you could use an introduction to make a bean implement an IsModified interface, to simplify caching.
Target object
Task is an object being advised by one or more aspects. Also referred to as the advised object.
Since Spring AOP is implemented using runtime proxies, this object will always be a proxied object.
AOP proxy
AOP proxy is an object created by the AOP framework in order to implement the aspect contracts (advise method executions and so on).
In the Spring Framework, an AOP proxy will be a JDK dynamic proxy or a CGLIB proxy. Proxy creation is transparent to users of the schema-based and @AspectJ styles of aspect declaration introduced in Spring 2.0.
Weaving
Weaving is to link aspects with other application types or objects to create an advised object.
This can be done at compile time (using the AspectJ compiler, for example), load time, or at runtime. Spring AOP, like other pure Java AOP frameworks, performs weaving at runtime.
AOP 101 with Java and AspectJ
Declare Aspect
Aspects classes are like any other normal bean, and annotated with @Aspect
package com.xyz.metrics.logging;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class MetricsAspect {
}
Declaring a PointCut
A PointCut helps in determining the join points (i.e. methods) of interest to be executed with different advices.
A pointcut has 2 parts:
- A PointCut expression that determines exactly which method executions we are interested in.
- A PointCut signature comprising a name and any number of parameters. The actual body of the method is irrelevant and in fact should be empty.
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.PointCut;
// expression
@PointCut("execution(* com.xyz.metrics.service.*(..))")
// signature
private void businessService() {}
For example, declare metric publishing API pointcut:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.PointCut;
@PointCut("execution(* .com.xyz.metrics.service.*(..))")
private void publishTimeMetrics() {}
Declaring Advices
Advices are declared using @{ADVICE-NAME} annotations
- @Before
- @After
- @AfterReturning
- @AfterThrowing
- @Around
package com.xyz.metrics.logging;
@Before("businessService()")
public void doBeforeTask(){
...
}
@After("businessService()")
public void doAfterTask(){
...
}
@AfterReturning(PointCut = "businessService()", returning = "retVal")
public void doAfterReturnningTask(Object retVal){
// you can intercept retVal here.
...
}
@AfterThrowing(PointCut = "businessService()", throwing = "ex")
public void doAfterThrowingTask(Exception ex){
// you can intercept thrown exception here.
...
}
@Around("businessService()")
public void doAroundTask(){
...
}
For example, declare metric publishing around API:
@AfterReturning(PointCut = "publishTimeMetrics()", returning = "retVal")
public void doAfterReturnningTask(Object retVal){
// you can intercept retVal here.
serviceCallMetrics.addCount(SERVICE_METRIC_SUCCESS_COUNT, 1, UNITS.ONE);
}
@AfterThrowing(PointCut = "publishTimeMetrics()", throwing = "ex")
public void doAfterThrowingTask(Exception ex){
// you can intercept thrown exception here.
serviceCallMetrics.addCount(SERVICE_METRIC_ERROR_COUNT, 1, UNITS.ONE);
}
@Around("publishTimeMetrics()")
public void doAroundTask(final ProceedingJoinPoint jp, final ServiceCallMetrics serviceCallMetrics)
throws Throwable {
//Get the start time
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
//run the business logic for API
jp.proceed();
//Log the success
//serviceCallMetrics.addCount(SERVICE_METRIC_SUCCESS_COUNT, 1, UNITS.ONE);
} catch (Exception exp) {
//Log the error
//serviceCallMetrics.addCount(SERVICE_METRIC_ERROR_COUNT, 1, UNITS.ONE);
throw exp
}
finally {
//Get the end time
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
//Log the time delta
serviceMetrics.addLevel(SERVICE_METRIC_LATENCY_NAME, endTime - startTime, SI.NANO(SI.SECOND));
}
}
The other way is to embed the pointcut:
@Around("execution(* com.xyz.metrics.service.*(..))")
public void doAroundTask(){
...
}
Define a business class
package com.xyz.metrics.service;
public class Shopper {
private Double amount;
private String name;
public void setAmount(Double total) {
this.amount = total;
}
public Integer getAmount() {
System.out.println("Total amount : " + amount );
return amount;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + name );
return name;
}
public void printThrowException(){
System.out.println("Exception raised");
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
Bean XML configuration:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd ">
<!-- For xml config -->
<!-- aop:config>
<aop:aspect id = "logmetrics" ref = "logging">
<aop:PointCut id = "selectAll"
expression = "execution(* com.xyz.metrics.service.*(..))"/>
<aop:after PointCut-ref = "selectAll" method = "doAroundTask"/>
<aop:after-returning PointCut-ref = "selectAll"
returning = "retVal"
method = "doAfterReturningTask"/>
<aop:after-throwing PointCut-ref = "selectAll"
throwing = "ex"
method = "AfterThrowingAdvice"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config -->
<!-- For AspectJ annotation -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<!-- Definition for shopper bean -->
<bean id = "shopper" class = "com.xyz.metrics.service">
<property name = "name" value = "Zara" />
<property name = "amount" value = "100"/>
</bean>
<!-- Definition for logging aspect -->
<bean id = "logging" class = "com.xyz.metrics.logging.MetricsAspect"/>
</beans>
Test AOP:
package com.xyz.metrics;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Shopper shopper = (Shopper) context.getBean("shopper");
shopper.getName();
shopper.getAmount();
shopper.printThrowException();
}
}